
It is natural that plant machinery and equipment will suffer from aging effects because of high temperature creep, fatigue, stress corrosion, erosion and simple wear either acting or in combination contribute to the gradual degradation of the affected component integrity.

The purpose of NDT-based condition assessment study is to evaluate the present condition of the components in terms of integrity & healthiness and to estimate future inspections, repairs, modifications / replacement based on projected usage with proper lead time, so that the economical operation of the unit can be optimized.

Various types of pressure vessels can be inspected using the Low Frequency Electromagnetic Technique (LFET). Using LFET, the actual wall plates can be inspected from inside or outside the pressure vessel. Welds can be tested for cracking through the usage of the Hawkeye Crack Detection System. Thus, a complete inspection of the pressure vessel can be performed. Our highly trained staff can also provide Dye Penetrant, Magnetic Particle, and Ultrasonic Inspection services.


Inspection and Certification of Lifting Tool Tackles for legal compliance (Form-10) of industries like D-Shackle, Bow Shackle, Wire Rope & Lifting Machine like EOT, CPB, HOT etc.


Onsite Inspection of Lift and hoist will be done by the qualified and experienced engineer for in various industries to evaluate the working condition. Also certification of the inspected equipment will be provided to complete the compliance of plant.


Ultrasonic Testing uses transmission of high frequency sound waves into a material to detect imperfections within the material or changes in material properties. The most commonly used ultrasonic testing method is Pulse Echo, wherein sound is introduced into the test object and reflections are returned to a receiver from internal imperfections and geometrical surfaces of the part.

Ultrasonic Testing uses transmission of high frequency sound waves into a material to detect imperfections within the material or changes in material properties. The most commonly used ultrasonic testing method is Pulse Echo, wherein sound is introduced into the test object and reflections are returned to a receiver from internal imperfections and geometrical surfaces of the part.

There are two different ferromagnetic examination media: dry particles and wet particles. Both forms can be either fluorescent or non-fluorescent (visible, colour contrast) and come in a variety of colours to contrast with the tested material.
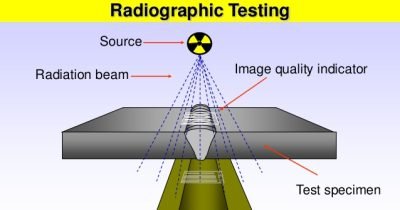
Radiographic Testing (RT), or industrial radiography, is a non-destructive testing(NDT) method of inspecting for hidden flaws/defects and to check the Homogeneity of Materials by using the ability of short wave length electromagnetic radiation (high energy Photons) to penetrate various materials as per standard ASTME-94-04, ASME Sec VIII Div-1 etc.

Liquid penetrant testing is probably the most widely used NDT method. The test object or material is coated with a visible or fluorescent dye solution. The excess dye is removed from the surface, and then a developer is applied. The developer acts like a blotter. It draws penetrant out of the imperfections which are open to the surface. With visible dyes, the vivid color contrast between the penetrant and the developer makes the bleed easy to see. An ultraviolet lamp is used to make the bled out fluorescent brightly, thus allowing the imperfection to be seen clearly.


In the field of industrial ultrasonic testing, Ultrasonic thickness measurement (UTM) is a method of performing non-destructive measurement (gauging) of the local thickness of a solid element (typically made of metal, if using ultrasound testing for industrial purposes) based on the time taken by the ultrasound wave to return to the surface. This type of measurement is typically performed with an ultrasonic thickness gauge.
UTM is frequently used to monitor metal thickness or weld quality in industrial settings such as mining. NDE technicians equipped with portable UTM probes reach steel plating in sides, Pipes. tanks, decks and the superstructure.
VibMaster helps the organization to track the deterioration for tanks, structure, pipes to make sure whether the condition of object is acceptable for use or not.

Eddy current testing is a non-destructive testing (NDT) inspection method used for a variety of purposes, including for flaw detection, material and coating thickness measurements, material identification and establishing the heat treatment condition of certain materials.


Surface-breaking defects
Linear defects (as small as 0.5mm deep and 5mm long)
Cracks
Lack of fusion
Generalised corrosion (particularly in the aircraft industry for the examination of aircraft skins)
Identification of both ferrous and non-ferrous metals and with certain alloys – in particular the aluminium alloys
Establishing the heat treatment condition
Determining whether a coating is non-conductive
Heat treat verification of metals
Positive Material Identification (PMI) is the analysis of a material, this can be any material but is generally used for the analysis of metallic alloy to establish composition by reading the quantities by percentage of its constituent elements.
PMI testing means that companies can make sure that every single part in their system meets specifications, critical replacement parts are the right alloy grade and all bought-in materials are exactly what they should be. This important step can be the key difference between seamless operations and catastrophic safety failures.


